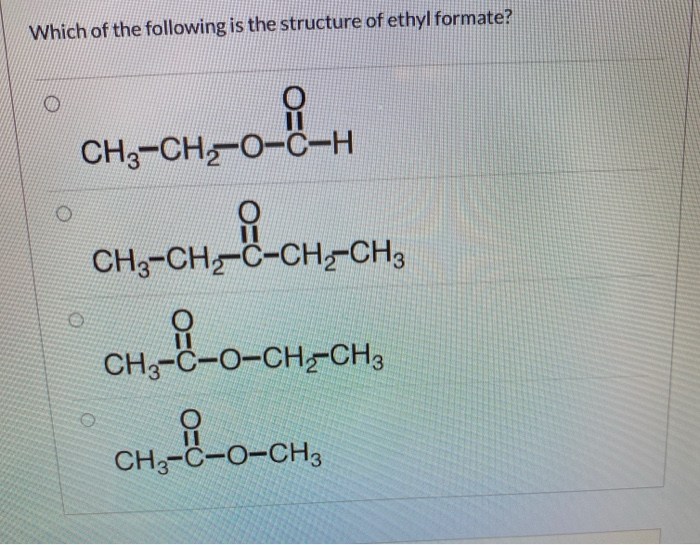
Fragmentation pattern of ethyl cinnamate
Fragmentation Pattern Of Ethyl Cinnamate. Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts. As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis.
 Simultaneous Determination Of 23 Flavor Additives In Tobacco Products Using Gas Chromatography Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Sciencedirect From sciencedirect.com
Simultaneous Determination Of 23 Flavor Additives In Tobacco Products Using Gas Chromatography Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Sciencedirect From sciencedirect.com
Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis.
The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL.
As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone. The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL.
 Source: people.whitman.edu
Source: people.whitman.edu
The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL. The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid. Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. As such MS-PCET can function as a non-classical mechanism for homolytic bond activation providing. The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step.
 Source: people.whitman.edu
Source: people.whitman.edu
We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid. The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL.
 Source: people.whitman.edu
Source: people.whitman.edu
Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid. Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts.

Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts. Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone. We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis.
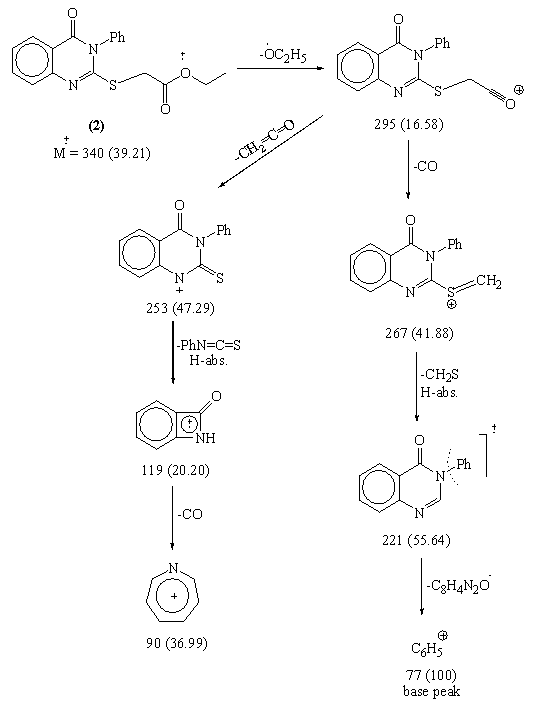 Source: article.sapub.org
Source: article.sapub.org
The cinnamic acid is then converted into coumaric acid by the action of cinnamate-4-hydroxylase C4H and subsequently converted into 4-coumaroil CoA by the 4-coumaroil CoA ligase 4CL. Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone.

Flavylium compounds are a well-known family of pigments because they are prevalent in the plant kingdom contributing to colors over a wide range from shades of yellow-red to blue in fruits flowers leaves and other plant parts. We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as.

Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone. Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone. MS-PCETs are redox mechanisms in which both an electron and a proton are exchanged together often in a concerted elementary step. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid.
 Source: people.whitman.edu
Source: people.whitman.edu
Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as. Following condensation of 4-coumaroil CoA with malonyl CoA naringenin chalcone is produced by chalcone. We present here a review of the photochemical and electrochemical applications of multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer MS-PCET in organic synthesis. HSCCC biphasic systems composed of n-butanolethyl acetate05 acetic acid. Flavylium compounds include a large variety of natural compound classes namely anthocyanins 3-deoxyanthocyanidins auronidins and their respective aglycones as.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title fragmentation pattern of ethyl cinnamate by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.