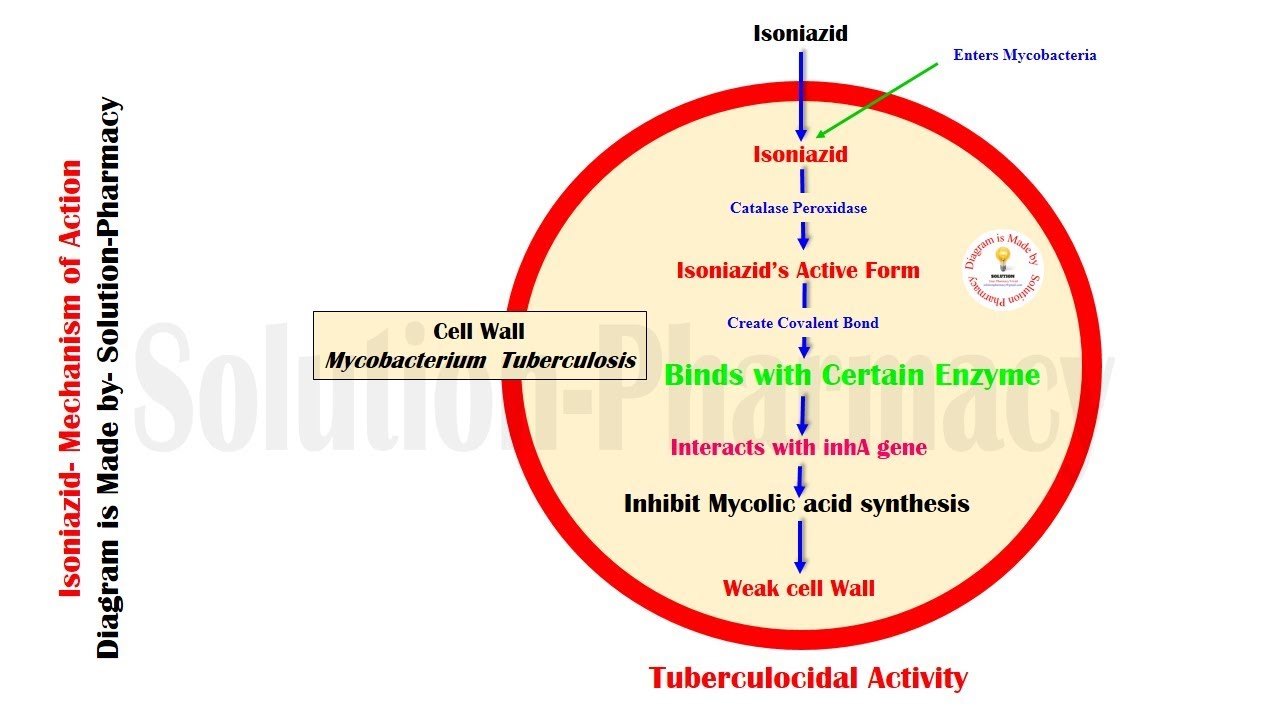
Isoniazid mechanism of action
Isoniazid Mechanism Of Action. Antibiotics are a class of drugs employed mainly against bacterial infections. Antibiotics are effective against either a small group of bacteria narrow-spectrum or a wide range. The rifamycins have a unique mechanism of action selectively inhibiting bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and show no cross-resistance with other antibiotics in clinical. Specficially activation is associated with reduction of the mycobacterial ferric KatG catalase-peroxidase by hydrazine and reaction with oxygen to form an oxyferrous enzyme complex.
 Mechanism Of Action Of Isoniazid Inh Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Mechanism Of Action Of Isoniazid Inh Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Although its mechanism of action is still unclear isoniazid appears to block the synthesis of mycolic acids major components of the mycobacterial cell wall. Antibiotics are a class of drugs employed mainly against bacterial infections. Specficially activation is associated with reduction of the mycobacterial ferric KatG catalase-peroxidase by hydrazine and reaction with oxygen to form an oxyferrous enzyme complex. Flecainide blocks fast inward sodium channels and slowly unbinds during diastole prolonging the refractory period of the heart. Isoniazid decreases effects of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Resistance in M.
Resistance to isoniazid occurs because of mutations in the katG inhA kasA and ahpC genes.
Once activated isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. Although its mechanism of action is still unclear isoniazid appears to block the synthesis of mycolic acids major components of the mycobacterial cell wall. When drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. Isoniazid is a prodrug that inhibits the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall. Resistance to isoniazid occurs because of mutations in the katG inhA kasA and ahpC genes. This agent is only active against actively growing mycobacteria because as a pro-drug it.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. 10 This blockade also shortens the duration of action potentials through the Purkinjie fibers. However the rate of treatment-limiting adverse events was higher in the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen. When drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. Antibiotics are effective against either a small group of bacteria narrow-spectrum or a wide range.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
This agent is only active against actively growing mycobacteria because as a pro-drug it. 10 This blockade also shortens the duration of action potentials through the Purkinjie fibers. The rifamycins have a unique mechanism of action selectively inhibiting bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and show no cross-resistance with other antibiotics in clinical. Resistance to isoniazid occurs because of mutations in the katG inhA kasA and ahpC genes. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Isoniazid is a synthetic derivative of nicotinic acid with anti-mycobacterial properties. Flecainide blocks fast inward sodium channels and slowly unbinds during diastole prolonging the refractory period of the heart. Mechanism Of Action. Some antibiotics are also used against parasitic infections. When drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Isoniazid decreases effects of metformin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Resistance in M. Mechanism Of Action. Flecainide blocks fast inward sodium channels and slowly unbinds during diastole prolonging the refractory period of the heart. Although its mechanism of action is still unclear isoniazid appears to block the synthesis of mycolic acids major components of the mycobacterial cell wall.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The rifamycins have a unique mechanism of action selectively inhibiting bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and show no cross-resistance with other antibiotics in clinical. Flecainide blocks fast inward sodium channels and slowly unbinds during diastole prolonging the refractory period of the heart. Antibiotics can have bacteriostatic ie stopping bacterial reproduction bactericidal ie killing bacteria or both mechanisms of action. Isoniazid is a prodrug that inhibits the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall. When drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
But the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen had higher rates of treatment completion and lower rates of hepatotoxicity. Specficially activation is associated with reduction of the mycobacterial ferric KatG catalase-peroxidase by hydrazine and reaction with oxygen to form an oxyferrous enzyme complex. KatG catalyzes the formation of the isonicotinic acyl radical which spontaneously couples with NADH to form the nicotinoyl-NAD adduct. Some antibiotics are also used against parasitic infections. Flecainide blocks fast inward sodium channels and slowly unbinds during diastole prolonging the refractory period of the heart.
 Source: bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Isoniazid is a prodrug that inhibits the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall. Patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control. Resistance in M. Antibiotics are effective against either a small group of bacteria narrow-spectrum or a wide range. When drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
 Source: pharmgkb.org
Source: pharmgkb.org
At therapeutic levels isoniazid is bactericidal against actively growing intracellular and extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms. Some antibiotics are also used against parasitic infections. Isoniazid is a prodrug and must be activated by bacterial catalase. When drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. Although its mechanism of action is still unclear isoniazid appears to block the synthesis of mycolic acids major components of the mycobacterial cell wall.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
But the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen had higher rates of treatment completion and lower rates of hepatotoxicity. Isoniazid is a synthetic derivative of nicotinic acid with anti-mycobacterial properties. Antibiotics are a class of drugs employed mainly against bacterial infections. Antibiotics can have bacteriostatic ie stopping bacterial reproduction bactericidal ie killing bacteria or both mechanisms of action. However the rate of treatment-limiting adverse events was higher in the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen.
 Source: clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com
Source: clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com
Isoniazid is a prodrug that inhibits the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall. Once activated isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. Antibiotics can have bacteriostatic ie stopping bacterial reproduction bactericidal ie killing bacteria or both mechanisms of action. Isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. KatG catalyzes the formation of the isonicotinic acyl radical which spontaneously couples with NADH to form the nicotinoyl-NAD adduct.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title isoniazid mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.