Mechanism of action valproic acid
Mechanism Of Action Valproic Acid. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action adverse event profile and other key factors eg off-label uses dosing pharmacodynamics pharmacokinetics monitoring relevant interactions pertinent for members of. Acetylsalicylic acid ASA blocks prostaglandin synthesis. In 1963 a serendipitous discovery was made by George Carraz during his investigations into the anticonvulsant effects of khelline when he found that all. 26 It enjoyed use as a popular organic solvent in industry and pharmaceutical manufacturing for nearly a century.
 Summary Of The Pharmacological Mechanism Of Action Of Valproic Acid Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Summary Of The Pharmacological Mechanism Of Action Of Valproic Acid Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. It is extensively used in the adult population to treat convulsions migraines and bipolar disorders. Okadaic acid C 44 H 68 O 13 is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. Possible decreased GI absorption andor increased renal clearance of valproic acid. 26 It enjoyed use as a popular organic solvent in industry and pharmaceutical manufacturing for nearly a century. It is non-selective for COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes 91011.
Due to the rapid onset and the extent of the decrease co-administration of carbapenem agents in patients stabilised on valproic acid should be avoided see.
Valproic acid 2-propylpentanoic acid. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. In 1963 a serendipitous discovery was made by George Carraz during his investigations into the anticonvulsant effects of khelline when he found that all. One of the primary causes of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning okadaic acid is a potent inhibitor of specific protein phosphatases and is known to have a variety of negative effects on cells. Although acute VPA intoxication frequently results in mild self-limited central nervous system depression serious. It is extensively used in the adult population to treat convulsions migraines and bipolar disorders.
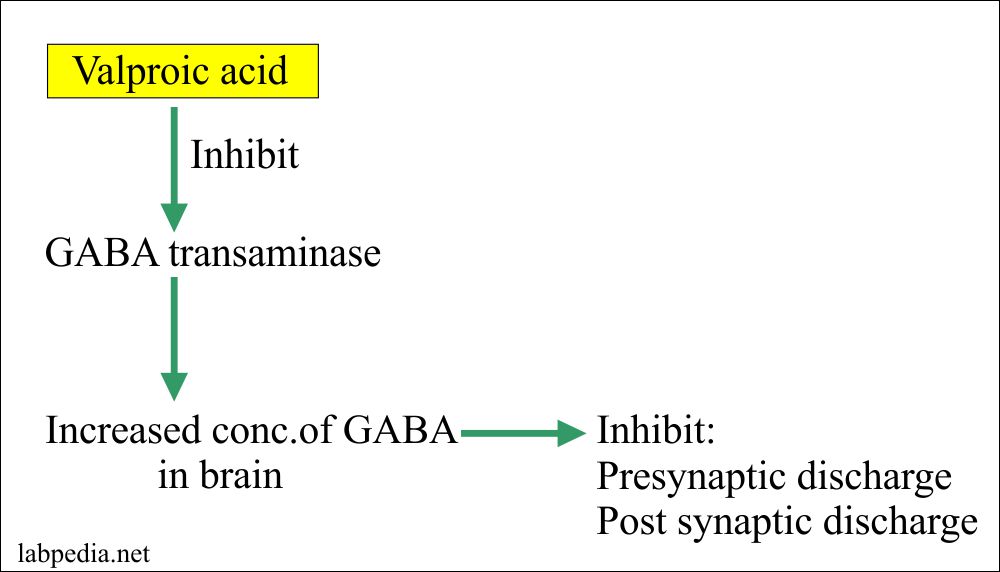 Source: labpedia.net
Source: labpedia.net
Inhibition of COX-1 results in the inhibition of platelet aggregation for about 7-10 days average platelet lifespan. Avoid coadministration of fedratinib a CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 substrate. Valproic acid 2-propylpentanoic acid. Possible decreased GI absorption andor increased renal clearance of valproic acid. Decreases in blood levels of valproic acid have been reported when it is co-administered with carbapenem agents resulting in a 60 100 decrease in valproic acid levels within two days sometimes associated with convulsions.
 Source: eurekaselect.com
Source: eurekaselect.com
Avoid coadministration of fedratinib a CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 substrate. Valproates precise mechanism of action is unclear. It is non-selective for COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes 91011. Valproic acid 2-propylpentanoic acid. It is a branched-chain saturated fatty acid and a branched-chain fatty acid.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Although acute VPA intoxication frequently results in mild self-limited central nervous system depression serious. Decreases in blood levels of valproic acid have been reported when it is co-administered with carbapenem agents resulting in a 60 100 decrease in valproic acid levels within two days sometimes associated with convulsions. VPA is a branched-chain carboxylic acid introduced as an anti-epileptic drug in 1978 in the United States. Inhibition of COX-1 results in the inhibition of platelet aggregation for about 7-10 days average platelet lifespan. Valproic acid is a branched-chain saturated fatty acid that comprises of a propyl substituent on a pentanoic acid stem.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It has a role as an anticonvulsant a GABA agent an EC 35198 histone deacetylase inhibitor a teratogenic agent a psychotropic drug a neuroprotective agent and an antimanic drug. A polyketide polyether derivative of a C 38 fatty. It is used to treat partial and generalized seizures and acute mania and as prophylaxis for bipolar disorder and migraine headaches. It is extensively used in the adult population to treat convulsions migraines and bipolar disorders. Inhibition of COX-1 results in the inhibition of platelet aggregation for about 7-10 days average platelet lifespan.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Although acute VPA intoxication frequently results in mild self-limited central nervous system depression serious. Valproate was first made in 1881 and came into medical use in 1962. Okadaic acid C 44 H 68 O 13 is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. Proposed mechanisms include affecting GABA levels blocking voltage-gated sodium channels and inhibiting histone deacetylases. Valproic acid is a branched-chain saturated fatty acid that comprises of a propyl substituent on a pentanoic acid stem.
 Source: exeley.com
Source: exeley.com
Valproic acid will increase the level or effect of fedratinib by Other see comment. Inhibition of COX-1 results in the inhibition of platelet aggregation for about 7-10 days average platelet lifespan. In 1963 a serendipitous discovery was made by George Carraz during his investigations into the anticonvulsant effects of khelline when he found that all. Valproate was first made in 1881 and came into medical use in 1962. Avoid coadministration of fedratinib a CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 substrate.
 Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Valproic acid will increase the level or effect of fedratinib by Other see comment. Valproic acid is an anticonvulsive and mood stabilizer medication. It is a branched-chain saturated fatty acid and a branched-chain fatty acid. Although acute VPA intoxication frequently results in mild self-limited central nervous system depression serious.
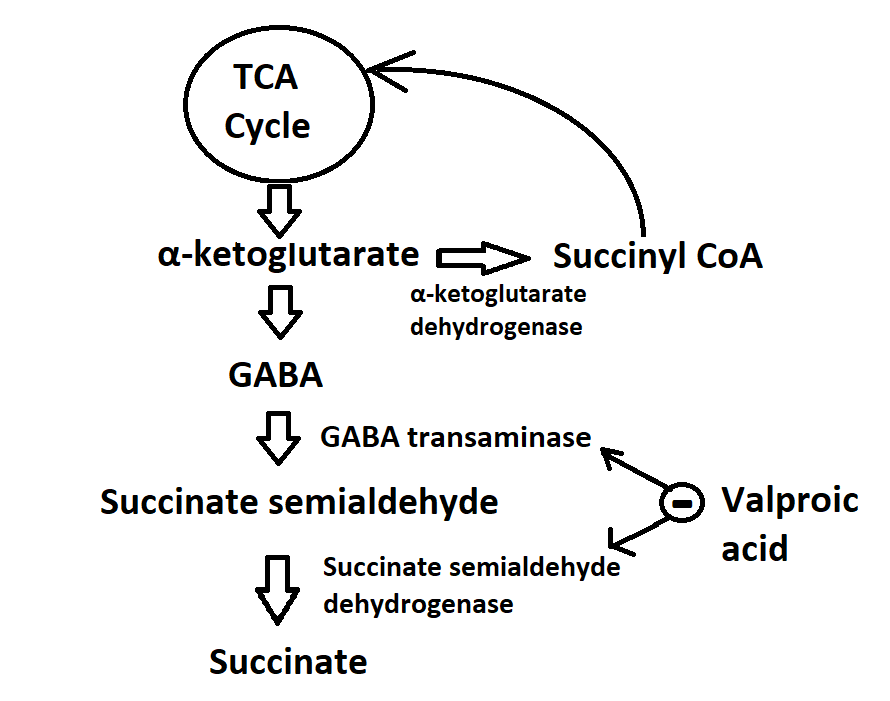
Valproates precise mechanism of action is unclear. A polyketide polyether derivative of a C 38 fatty. Although acute VPA intoxication frequently results in mild self-limited central nervous system depression serious. Okadaic acid C 44 H 68 O 13 is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It is extensively used in the adult population to treat convulsions migraines and bipolar disorders. Valproic acid is a branched-chain saturated fatty acid that comprises of a propyl substituent on a pentanoic acid stem. 26 It enjoyed use as a popular organic solvent in industry and pharmaceutical manufacturing for nearly a century. Valproates precise mechanism of action is unclear. It is extensively used in the adult population to treat convulsions migraines and bipolar disorders.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Okadaic acid C 44 H 68 O 13 is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. It has a role as an anticonvulsant a GABA agent an EC 35198 histone deacetylase inhibitor a teratogenic agent a psychotropic drug a neuroprotective agent and an antimanic drug. It is non-selective for COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes 91011. Valproic acid is an anticonvulsive and mood stabilizer medication. Valproic acid is a branched short-chain fatty acid SCFA made from valeric acid.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title mechanism of action valproic acid by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.