Nitrofurantoin mechanism of action
Nitrofurantoin Mechanism Of Action. Pulmonary toxicity is attributed. Mechanism of Action. Nitrofurantoin is a broad spectrum antibacterial agent active against the majority of urinary pathogens. The wide range of organisms sensitive to the bactericidal activity include.
 Adverse Effects Of Chronic Nitrofurantoin Therapy In Women With Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In An Outpatient Setting Springerlink From link.springer.com
Adverse Effects Of Chronic Nitrofurantoin Therapy In Women With Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In An Outpatient Setting Springerlink From link.springer.com
Mafenide works by reducing the bacterial population present in the avascular tissues of burns and permits spontaneous healing of deep partial-thickness burns. Pulmonary toxicity is attributed. Development of antinuclear antibodies and antismooth muscle antibodies has also been reported. The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. Specifically Kanamycin binds to four nucleotides of 16S rRNA and a single amino acid of protein S12. As a result of such inactivations the vital biochemical processes of protein synthesis aerobic energy metabolism DNA synthesis RNA.
As a result of such inactivations the vital biochemical processes of protein synthesis aerobic energy metabolism DNA synthesis RNA.
As a result of such inactivations the vital biochemical processes of protein synthesis aerobic energy metabolism DNA synthesis RNA. Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. The wide range of organisms sensitive to the bactericidal activity include. Nitrofurantoin is a nitrofuran antimicrobial agent with activity against certain Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Specifically Kanamycin binds to four nucleotides of 16S rRNA and a single amino acid of protein S12.
 Source: biopharmanotes.com
Source: biopharmanotes.com
Nitrofurantoin exerts greater effects on bacterial cells than mammalian cells because bacterial cells activate the drug more rapidly. Escherichia coli strain K12. As a result of such inactivations the vital biochemical processes of protein synthesis aerobic energy. Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. Wait until Abx Tx complete to administer live bacterial vaccine. Mechanism of action. This section does not cite any sources. Nitrofurantoin decreases effects of BCG vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Nitrofurantoin is converted by bacterial nitroreductases to electrophilic intermediates which inhibit the citric acid cycle as well as synthesis of DNA RNA and protein. Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. Nitrofurantoin decreases effects of BCG vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Mafenide works by reducing the bacterial population present in the avascular tissues of burns and permits spontaneous healing of deep partial-thickness burns.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Wait until Abx Tx complete to administer live bacterial vaccine. Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. Avoid coadministration of cholera vaccine with systemic antibiotics since these agents may be active against the vaccine. Development of antinuclear antibodies and antismooth muscle antibodies has also been reported.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
This interferes with decoding site in the vicinity of nucleotide 1400 in 16S rRNA of 30S subunit. Pulmonary toxicity is attributed. Avoid coadministration of cholera vaccine with systemic antibiotics since these agents may be active against the vaccine. The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. This region interacts with the wobble base in the anticodon of tRNA.
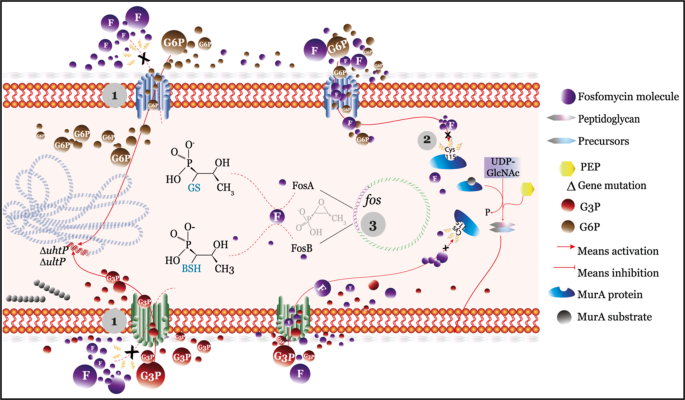 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Escherichia coli strain K12. Mechanism of action. Nitrofurantoin causes hepatic injury acute and chronic through an immunological or metabolic mechanism. This interferes with decoding site in the vicinity of nucleotide 1400 in 16S rRNA of 30S subunit. Mechanism of Action.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The broad mechanism of action for this drug likely is responsible for the low development of resistance to its effects as the drug affects many. The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. This region interacts with the wobble base in the anticodon of tRNA. Nitrofurantoin decreases effects of BCG vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Nitrofurantoin exerts greater effects on bacterial cells than mammalian cells because bacterial cells activate the drug more rapidly.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. Mechanism of action. This section does not cite any sources. The broad mechanism of action for this drug likely is responsible for the low development of resistance to its effects as the drug affects many. It is not known which of the actions of nitrofurantoin is primarily responsible for its bactericidal activity.
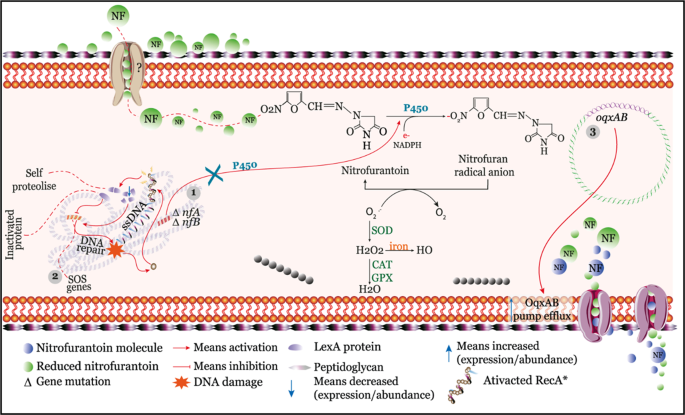 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. This interferes with decoding site in the vicinity of nucleotide 1400 in 16S rRNA of 30S subunit. Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. Pulmonary toxicity is attributed. As a result of such inactivations the vital biochemical processes of protein synthesis aerobic energy metabolism DNA synthesis RNA.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Mechanism of action. The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of nitrofurantoin is unusual among antibacterials. As a result of such inactivations the vital biochemical processes of protein synthesis aerobic energy. Nitrofurantoin is a nitrofuran antimicrobial agent with activity against certain Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. A Probable pyruvate-flavodoxin oxidoreductase.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title nitrofurantoin mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.