Nitrous oxide mechanism of action
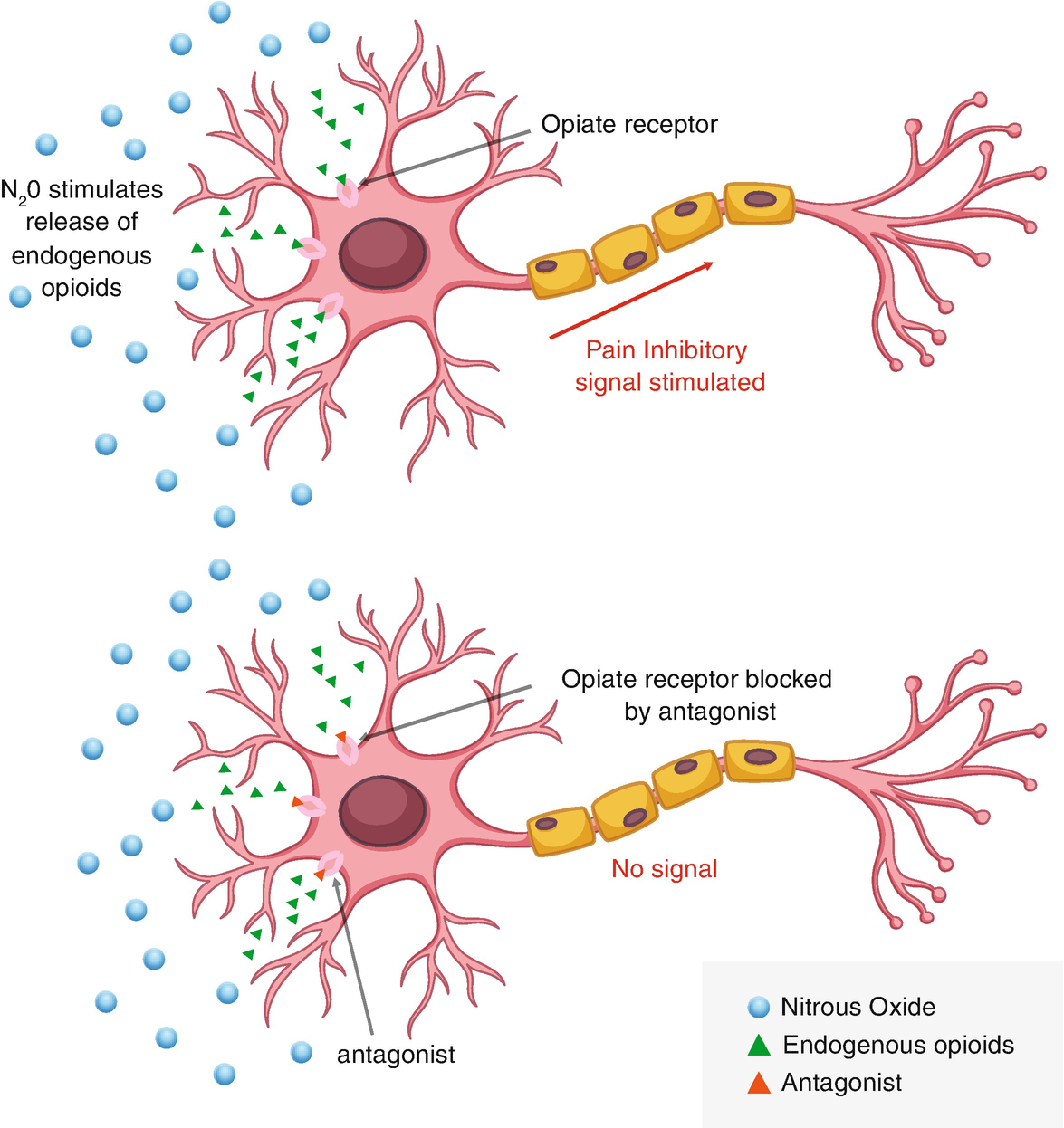
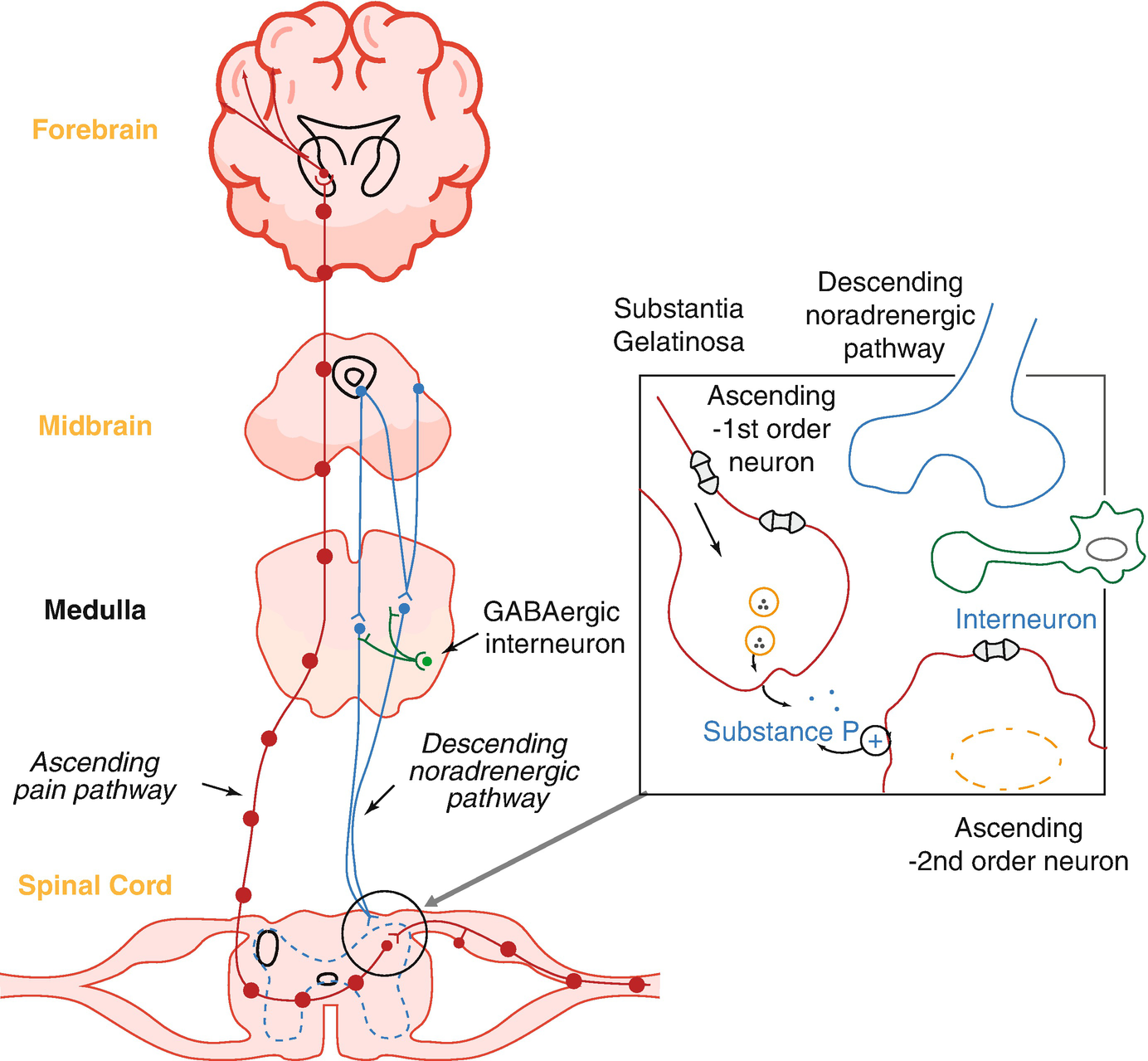
Nitrous Oxide Mechanism Of Action. The mode of action of nitrous oxide is still unclear. Findings to date indicate that nitrous oxide induces opioid peptide release in the brain stem leading to the activation of descending noradrenergic neurones which results in modulation of the nociceptive process in the spinal cord. Reactions With di- and triatomic molecules. It can be manufactured and used for a variety of things such as a pharmacologic agent to produce anesthesia a food additive as a propellant and an additive to fuels to increase available oxygen in combustion.
 Mini Review A Brief History Of Nitrous Oxide N2o Use In Neuropsychiatry Bentham Science From eurekaselect.com
Mini Review A Brief History Of Nitrous Oxide N2o Use In Neuropsychiatry Bentham Science From eurekaselect.com
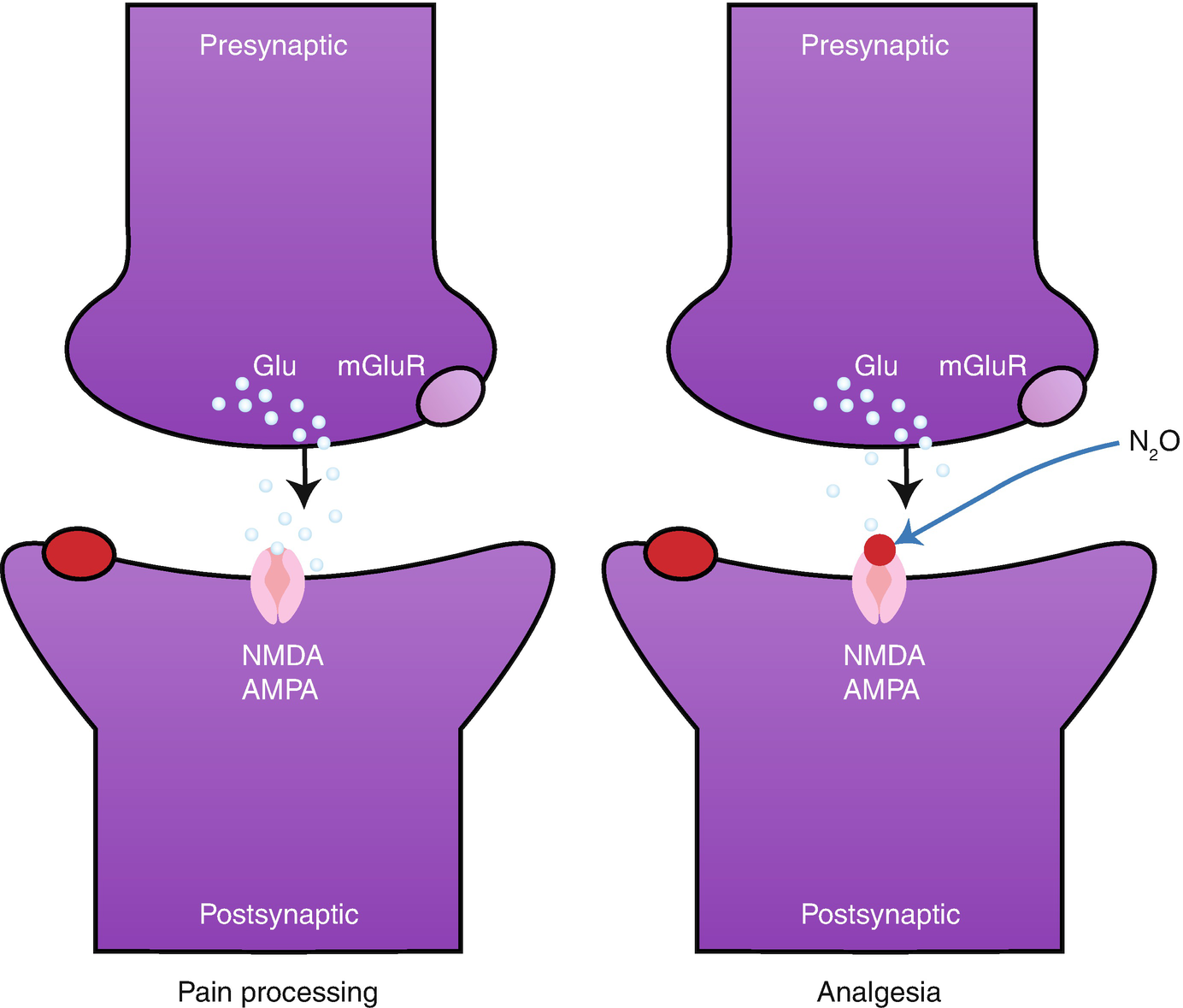
Depending on their mechanism of photosynthesis. Inhaled anesthetics enjoy regular use in the clinical setting due to chemical. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. It has been suggested that its general anaesthetic actions are due to blockade of the NMDA subtype of the glutamate receptor and its analgesic actions may come from stimulation of opioid receptors but neither of these are yet proven in humans. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. Findings to date indicate that nitrous oxide induces opioid peptide release in the brain stem leading to the activation of descending noradrenergic neurones which results in modulation of the nociceptive process in the spinal cord.
Conversely α 2-adrenoceptor antagonists block the pain-reducing effects of N 2 O when given directly to the spinal cord but.
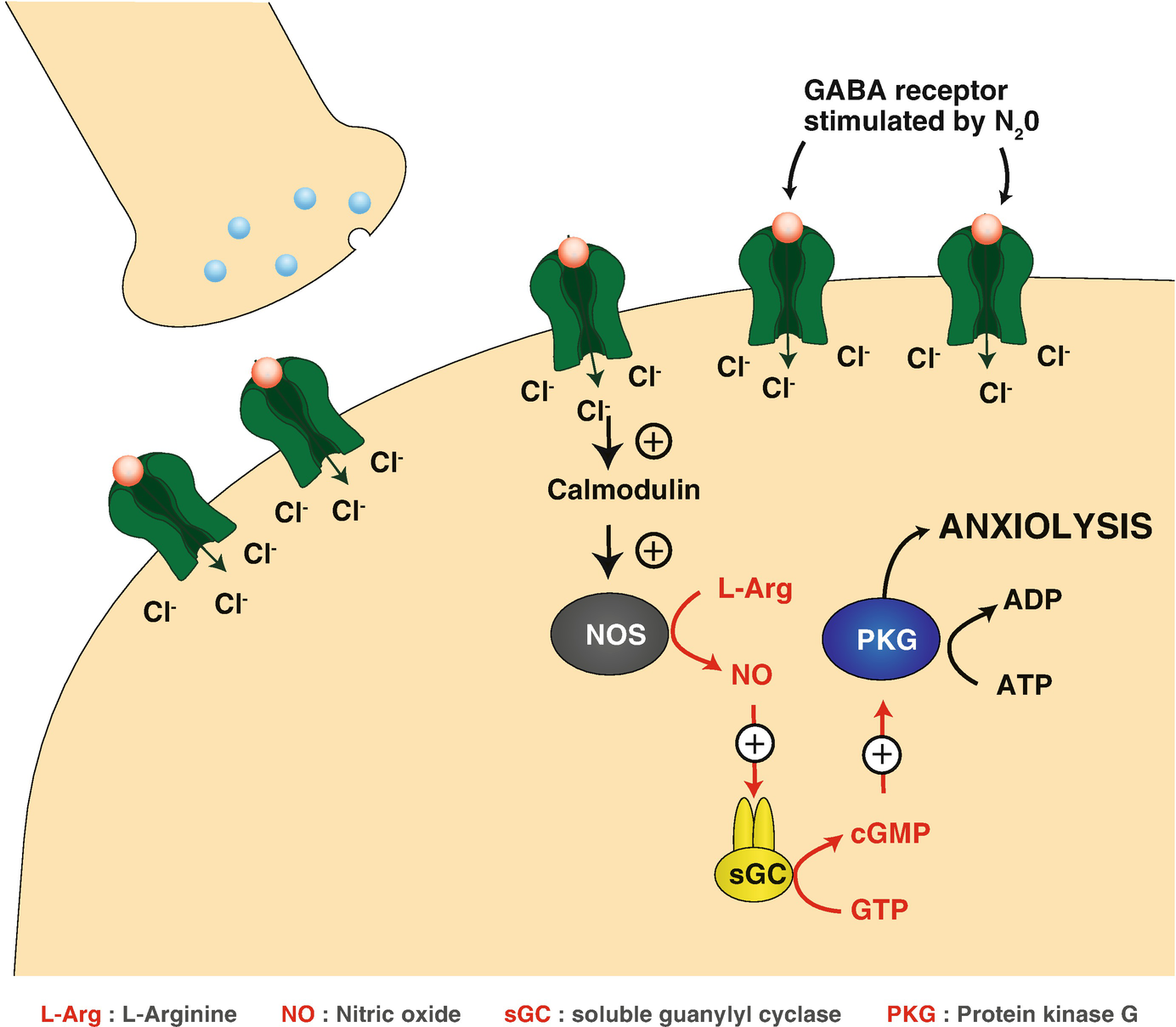
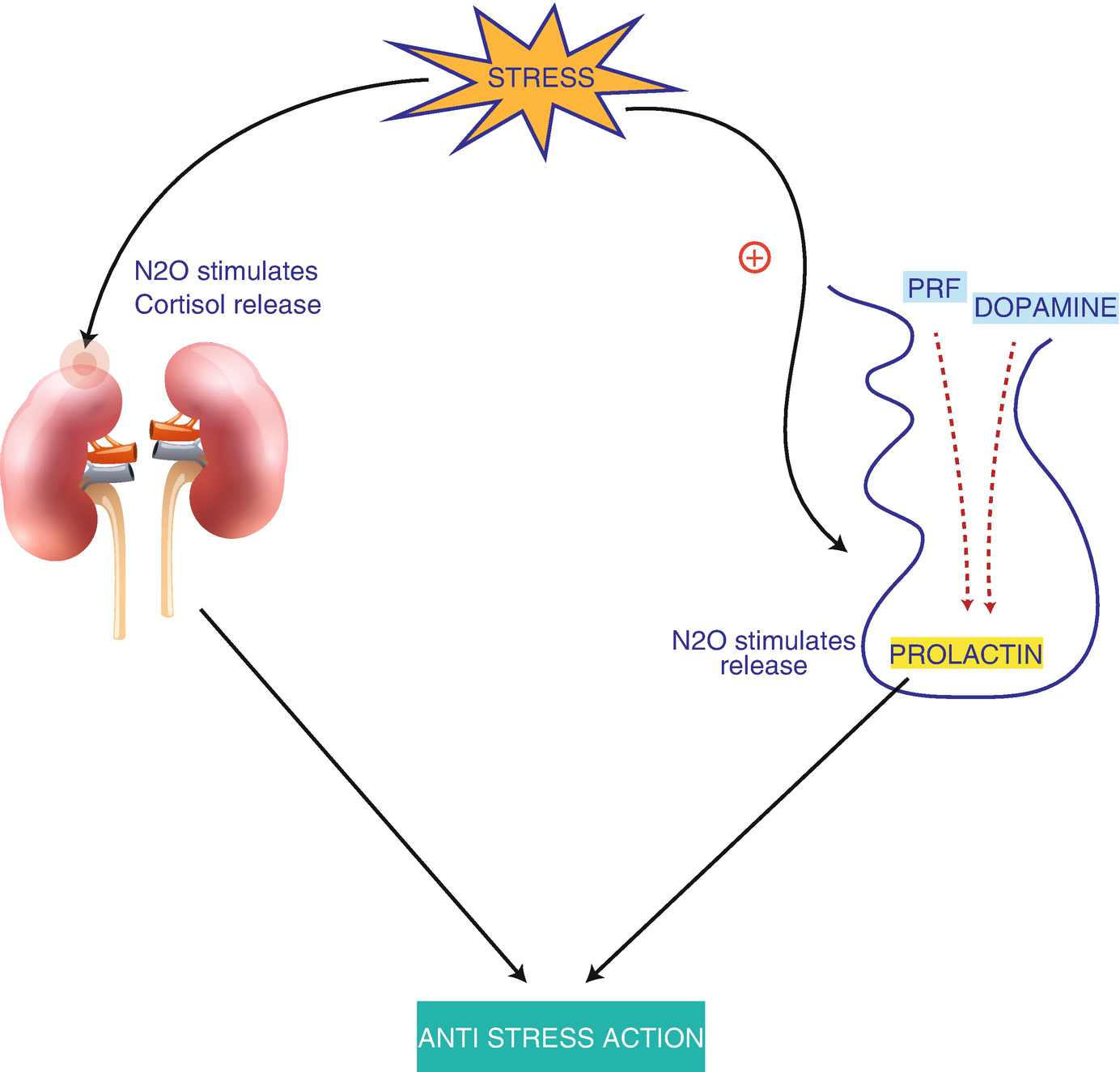
Apart from an indirect action nitrous oxide like morphine also interacts directly with the endogenous opioid system by binding at opioid receptor binding sites. The mechanism of action is believed to be a nonspecific effect on the fluidity of neuronal membranes and NDMA ion channels. The recreational effects occur at lower concentrations and may be produced by alterations in brain. Natural causes such as changes in solar radiation or volcanic activity are estimated to have contributed less than plus or minus 01C to total warming between 1890 and 2010. Upon condensing to a liquid nitric oxide dimerizes to dinitrogen dioxide but the association is weak and reversible. Metoprolol is a beta-1-adrenergic receptor inhibitor specific to cardiac cells with negligible effect on beta-2 receptors.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
It can be manufactured and used for a variety of things such as a pharmacologic agent to produce anesthesia a food additive as a propellant and an additive to fuels to increase available oxygen in combustion. Perhaps the best-known use of nitrous oxide in medical history is its use as an anesthetic. Upon condensing to a liquid nitric oxide dimerizes to dinitrogen dioxide but the association is weak and reversible. It has been suggested that its general anaesthetic actions are due to blockade of the NMDA subtype of the glutamate receptor and its analgesic actions may come from stimulation of opioid receptors but neither of these are yet proven in humans. Anesthetic gases nitrous oxide halothane isoflurane desflurane sevoflurane also known as inhaled anesthetics are administered as primary therapy for preoperative sedation and adjunctive anesthesia maintenance to intravenous IV anesthetic agents ie midazolam propofol in the perioperative setting.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Anesthetic gases nitrous oxide halothane isoflurane desflurane sevoflurane also known as inhaled anesthetics are administered as primary therapy for preoperative sedation and adjunctive anesthesia maintenance to intravenous IV anesthetic agents ie midazolam propofol in the perioperative setting. The belief that inhalants such as whipit cause a head rush or floaty feeling by depriving the brain of oxygen is a misconception. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. 1 This is the likely mechanism for adverse health effects reported in those individuals who are chronically exposed to trace amounts of the drug such as infertility spontaneous abortion blood dyscrasias and neurologic deficits. Upon condensing to a liquid nitric oxide dimerizes to dinitrogen dioxide but the association is weak and reversible.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Inhaled anesthetics enjoy regular use in the clinical setting due to chemical. It has been suggested that its general anaesthetic actions are due to blockade of the NMDA subtype of the glutamate receptor and its analgesic actions may come from stimulation of opioid receptors but neither of these are yet proven in humans. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. Several receptoreffector mechanisms including dopamine receptors α2 adrenoceptors benzodiazepine receptors and -methyl- -aspartate NMDA. Natural causes such as changes in solar radiation or volcanic activity are estimated to have contributed less than plus or minus 01C to total warming between 1890 and 2010.
 Source: eurekaselect.com
Source: eurekaselect.com
Apart from an indirect action nitrous oxide like morphine also interacts directly with the endogenous opioid system by binding at opioid receptor binding sites. 1 This is the likely mechanism for adverse health effects reported in those individuals who are chronically exposed to trace amounts of the drug such as infertility spontaneous abortion blood dyscrasias and neurologic deficits. The pharmacological mechanism of action of N 2 O in medicine is not fully known. Several receptoreffector mechanisms including dopamine receptors α2 adrenoceptors benzodiazepine receptors and -methyl- -aspartate NMDA. The NN distance in crystalline NO is 218 pm nearly twice the NO distance.
 Source: library.med.utah.edu
Source: library.med.utah.edu
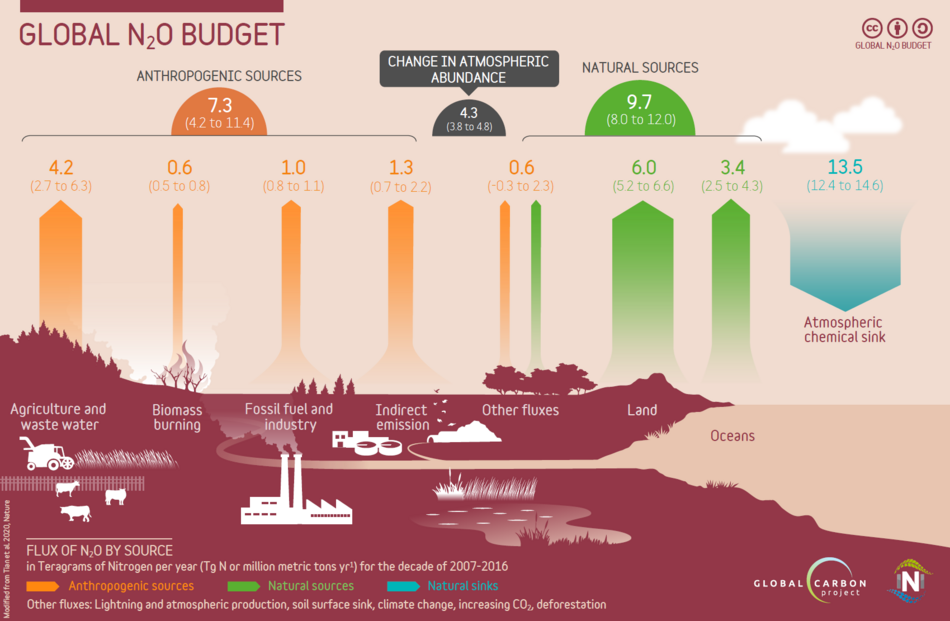
Apart from an indirect action nitrous oxide like morphine also interacts directly with the endogenous opioid system by binding at opioid receptor binding sites. Nitrous Oxide N 2 O A powerful greenhouse gas with a global warming potential of 298 times that of carbon dioxide CO 2. Nitrous Oxide is a naturally occurring gas that is colorless and non flammable. Several receptoreffector mechanisms including dopamine receptors α2 adrenoceptors benzodiazepine receptors and -methyl- -aspartate NMDA. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Nitrous Oxide N 2 O A powerful greenhouse gas with a global warming potential of 298 times that of carbon dioxide CO 2. Depending on their mechanism of photosynthesis. The belief that inhalants such as whipit cause a head rush or floaty feeling by depriving the brain of oxygen is a misconception. Several receptoreffector mechanisms including dopamine receptors α2 adrenoceptors benzodiazepine receptors and -methyl- -aspartate NMDA. Natural causes such as changes in solar radiation or volcanic activity are estimated to have contributed less than plus or minus 01C to total warming between 1890 and 2010.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The mode of action of nitrous oxide is still unclear. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. It has been suggested that its general anaesthetic actions are due to blockade of the NMDA subtype of the glutamate receptor and its analgesic actions may come from stimulation of opioid receptors but neither of these are yet proven in humans. A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Reactions With di- and triatomic molecules. The pharmacological mechanism of action of N 2 O in medicine is not fully known. Nitrous Oxide is a naturally occurring gas that is colorless and non flammable. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. The GWP is from the.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Natural causes such as changes in solar radiation or volcanic activity are estimated to have contributed less than plus or minus 01C to total warming between 1890 and 2010. The recreational effects occur at lower concentrations and may be produced by alterations in brain. The GWP is from the. Nitrous Oxide N 2 O A powerful greenhouse gas with a global warming potential of 298 times that of carbon dioxide CO 2. Depending on their mechanism of photosynthesis.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Several receptoreffector mechanisms including dopamine receptors α2 adrenoceptors benzodiazepine receptors and -methyl- -aspartate NMDA. Nitrous oxide irreversibly oxidizes vitamin B12 reducing the activity of B12-dependent enzymes such as methionine and thymidylate synthetases. Nitrous oxide like CO 2 is a long-lived greenhouse gas that accumulates in the atmosphere over decades to centuries. Perhaps the best-known use of nitrous oxide in medical history is its use as an anesthetic. Nitric oxide should not be confused with nitrogen dioxide NO 2 a brown gas and major air pollutant nor with nitrous oxide N 2 O an anesthetic.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title nitrous oxide mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






