Oxazepam mechanism of action
Oxazepam Mechanism Of Action. Unlike benzodiazepines etifoxine may produce its anxiolytic effects through a dual mechanism by directly binding to GABA A receptors and purportedly exact binding site undetermined to the mitochondrial translocator protein TSPO resulting in increases in endogenous neurosteroids. A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. Specifically Kanamycin binds to four nucleotides of 16S rRNA and a single amino acid of protein S12. Clonazepams primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain by the benzodiazepine receptor located on GABA A receptors which in turn leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing.
 Anti Anxiety Drugs Online Presentation From en.ppt-online.org
Anti Anxiety Drugs Online Presentation From en.ppt-online.org
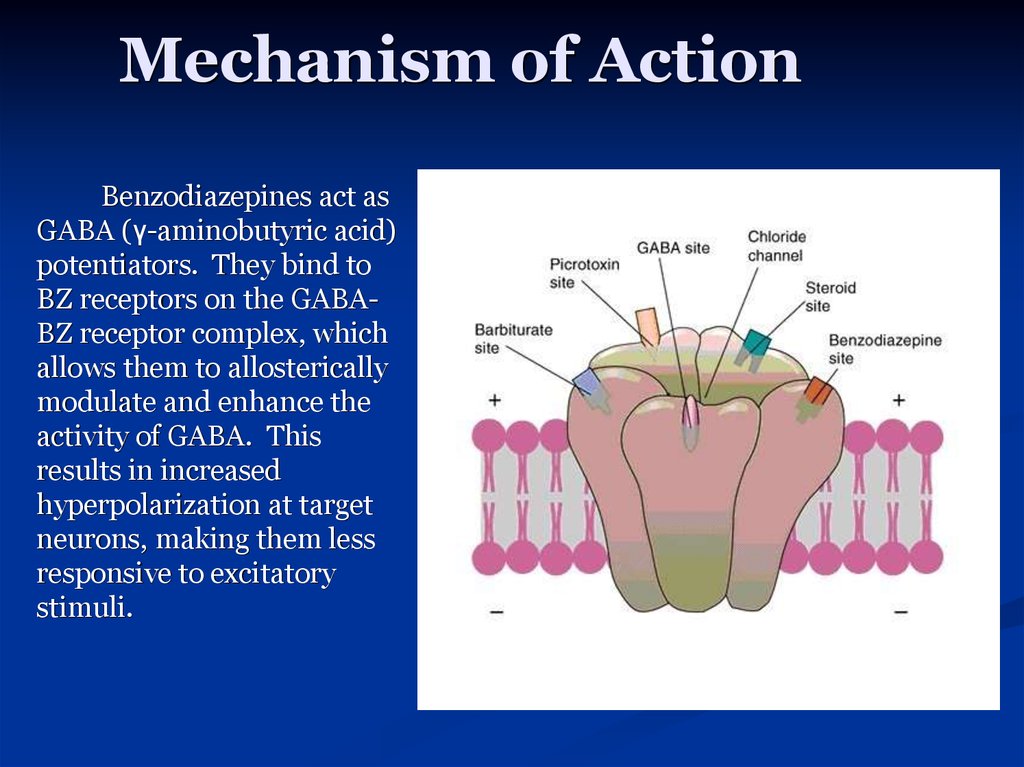
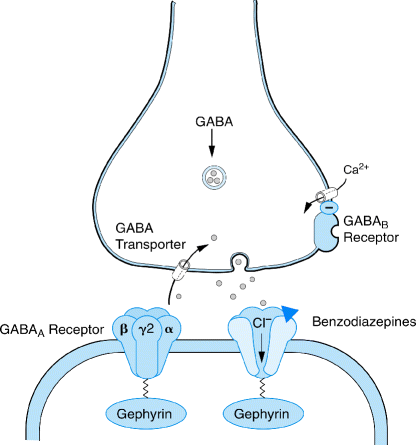
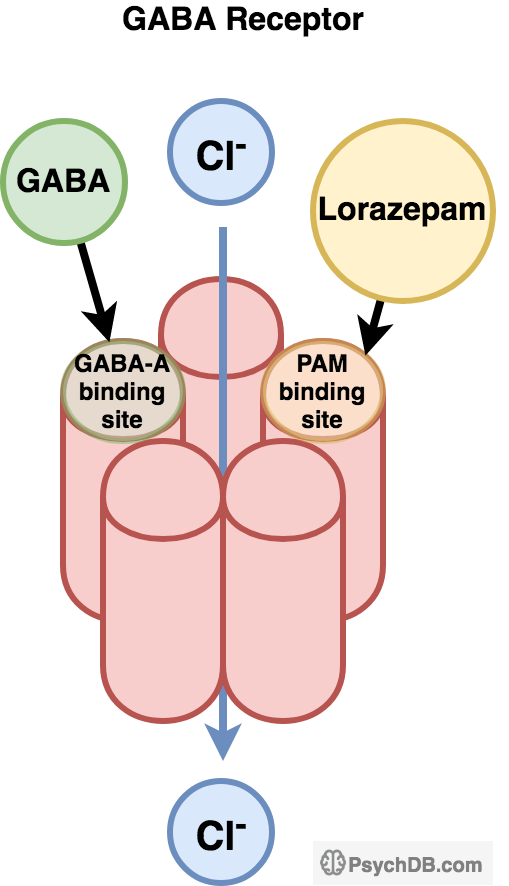
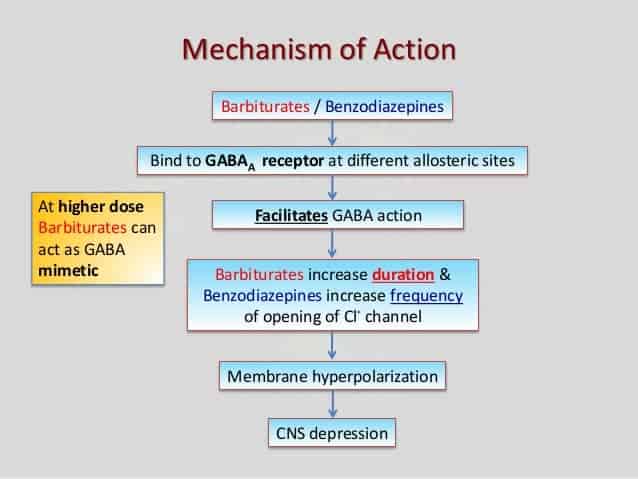
Unlike benzodiazepines etifoxine may produce its anxiolytic effects through a dual mechanism by directly binding to GABA A receptors and purportedly exact binding site undetermined to the mitochondrial translocator protein TSPO resulting in increases in endogenous neurosteroids. Metoprolol is a beta-1-adrenergic receptor inhibitor specific to cardiac cells with negligible effect on beta-2 receptors. This region interacts with the wobble base in the anticodon of tRNA. Benzodiazepines do not replace GABA but instead enhance the effect of GABA at the GABA A receptor by increasing the opening frequency of chloride ion channels which. This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Mechanism of Action Benzodiazepines increase frequency of opening of Cl- channels induced by GABA GABA facilitatory action increase binding of GABA to GABAA receptor Barbiturates increase duration of opening of Cl- channels induced by GABA.
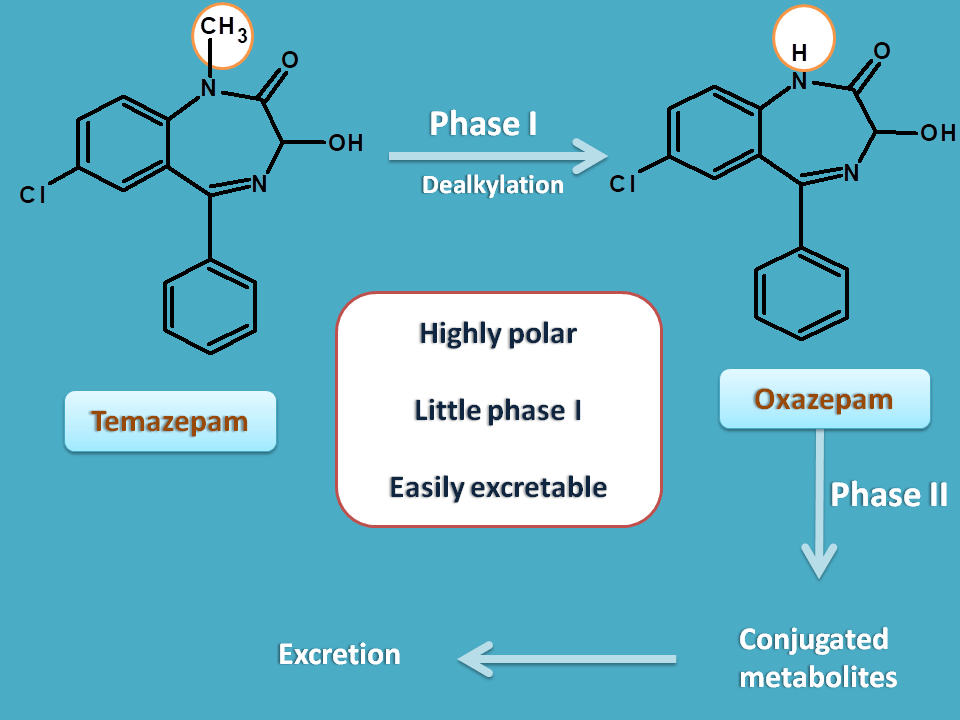
Oxazepam Temazepam Lorazepam Out the Liver.
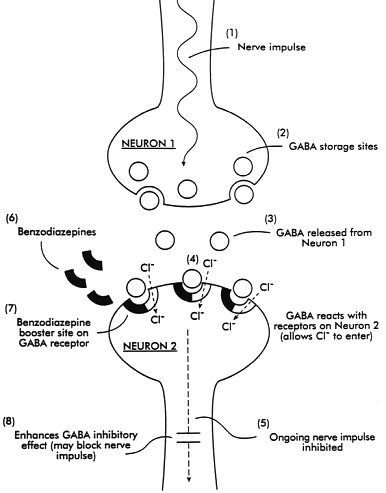
Benzodiazepines do not replace GABA but instead enhance the effect of GABA at the GABA A receptor by increasing the opening frequency of chloride ion channels which. 7- Muscular disorders. This interferes with decoding site in the vicinity of nucleotide 1400 in 16S rRNA of 30S subunit. Metoprolol is a beta-1-adrenergic receptor inhibitor specific to cardiac cells with negligible effect on beta-2 receptors. This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Mechanism of action.
 Source: cambridge.org
Source: cambridge.org
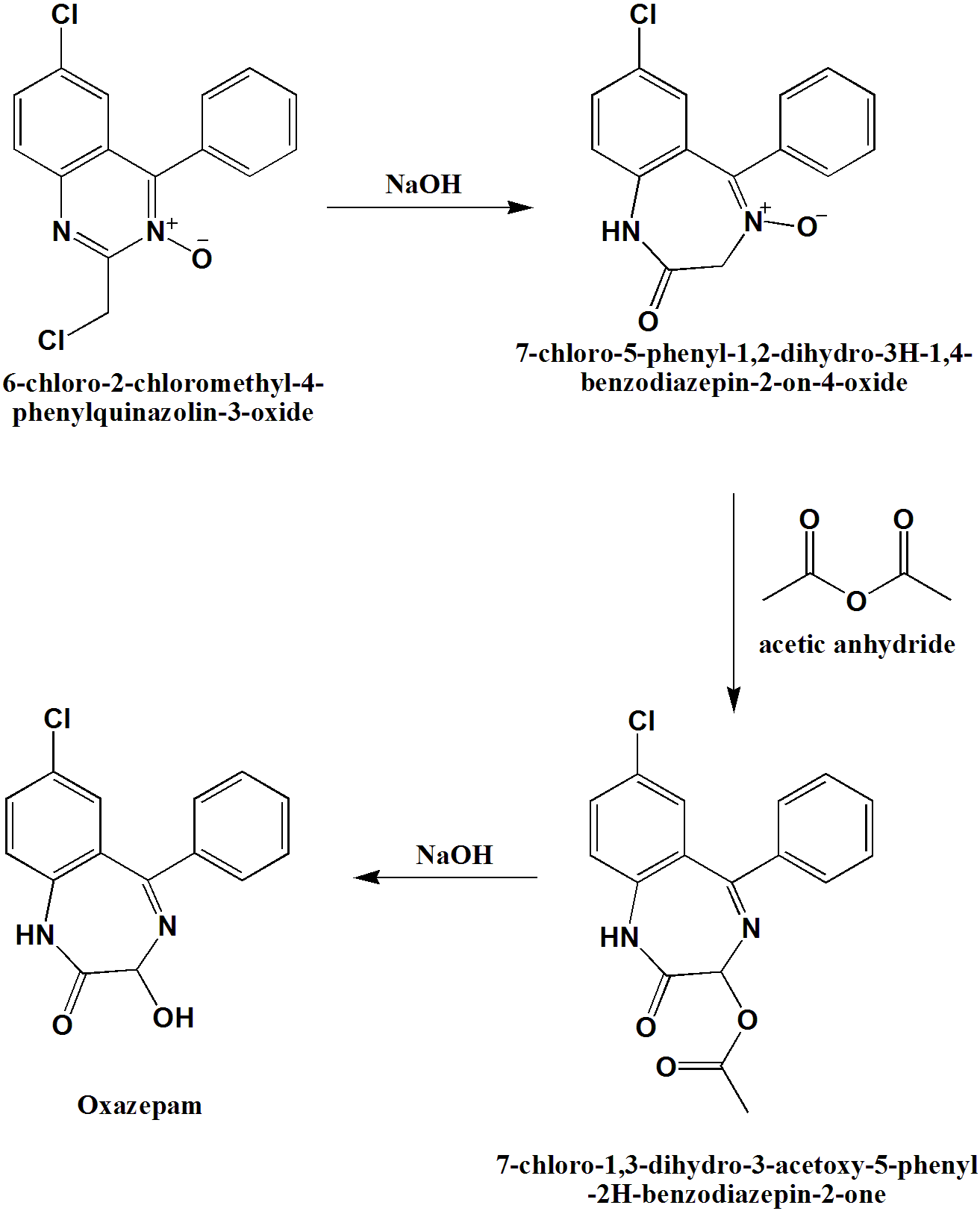
Aminoglycosides like kanamycin irreversibly bind to specific 30S-subunit proteins and 16S rRNA. Mechanism of action. Mechanism of Action Characteristics and Effects. This interferes with decoding site in the vicinity of nucleotide 1400 in 16S rRNA of 30S subunit. On the other hand oxazepam is the benzodiazepine most used in the treatment of severe withdrawal syndromes and in patients who metabolize drugs with greater difficulty such as the elderly or those with cirrhosis of the liver.
 Source: en.ppt-online.org
Source: en.ppt-online.org
Benzodiazepines do not replace GABA but instead enhance the effect of GABA at the GABA A receptor by increasing the opening frequency of chloride ion channels which. Mechanism of Action Characteristics and Effects. Mechanism of action. Three BZDs undergo extrahepatic metabolism and do not form active metabolites. Oxazepam Temazepam Lorazepam Out the Liver.
 Source: psychdb.com
Source: psychdb.com
A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. Three BZDs undergo extrahepatic metabolism and do not form active metabolites. This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Mechanism of Action Characteristics and Effects.
 Source: medicoapps.org
Source: medicoapps.org
This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Oxazepam Temazepam Lorazepam Out the Liver. Metoprolol is a beta-1-adrenergic receptor inhibitor specific to cardiac cells with negligible effect on beta-2 receptors. On the other hand oxazepam is the benzodiazepine most used in the treatment of severe withdrawal syndromes and in patients who metabolize drugs with greater difficulty such as the elderly or those with cirrhosis of the liver. Mechanism of Action Benzodiazepines increase frequency of opening of Cl- channels induced by GABA GABA facilitatory action increase binding of GABA to GABAA receptor Barbiturates increase duration of opening of Cl- channels induced by GABA.
 Source: benzo.org.uk
Source: benzo.org.uk
Clonazepams primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain by the benzodiazepine receptor located on GABA A receptors which in turn leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing. A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. This region interacts with the wobble base in the anticodon of tRNA. Unlike benzodiazepines etifoxine may produce its anxiolytic effects through a dual mechanism by directly binding to GABA A receptors and purportedly exact binding site undetermined to the mitochondrial translocator protein TSPO resulting in increases in endogenous neurosteroids. Three BZDs undergo extrahepatic metabolism and do not form active metabolites.
 Source: gpatindia.com
Source: gpatindia.com
Mechanism of action. Clonazepams primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain by the benzodiazepine receptor located on GABA A receptors which in turn leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing. Metoprolol is a beta-1-adrenergic receptor inhibitor specific to cardiac cells with negligible effect on beta-2 receptors. Benzodiazepines do not replace GABA but instead enhance the effect of GABA at the GABA A receptor by increasing the opening frequency of chloride ion channels which. Oxazepam Temazepam Lorazepam Out the Liver.
This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Specifically Kanamycin binds to four nucleotides of 16S rRNA and a single amino acid of protein S12. This region interacts with the wobble base in the anticodon of tRNA. This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. On the other hand oxazepam is the benzodiazepine most used in the treatment of severe withdrawal syndromes and in patients who metabolize drugs with greater difficulty such as the elderly or those with cirrhosis of the liver.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Mechanism of Action Characteristics and Effects. Oxazepam Temazepam Lorazepam Out the Liver. A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. Clonazepams primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain by the benzodiazepine receptor located on GABA A receptors which in turn leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing.
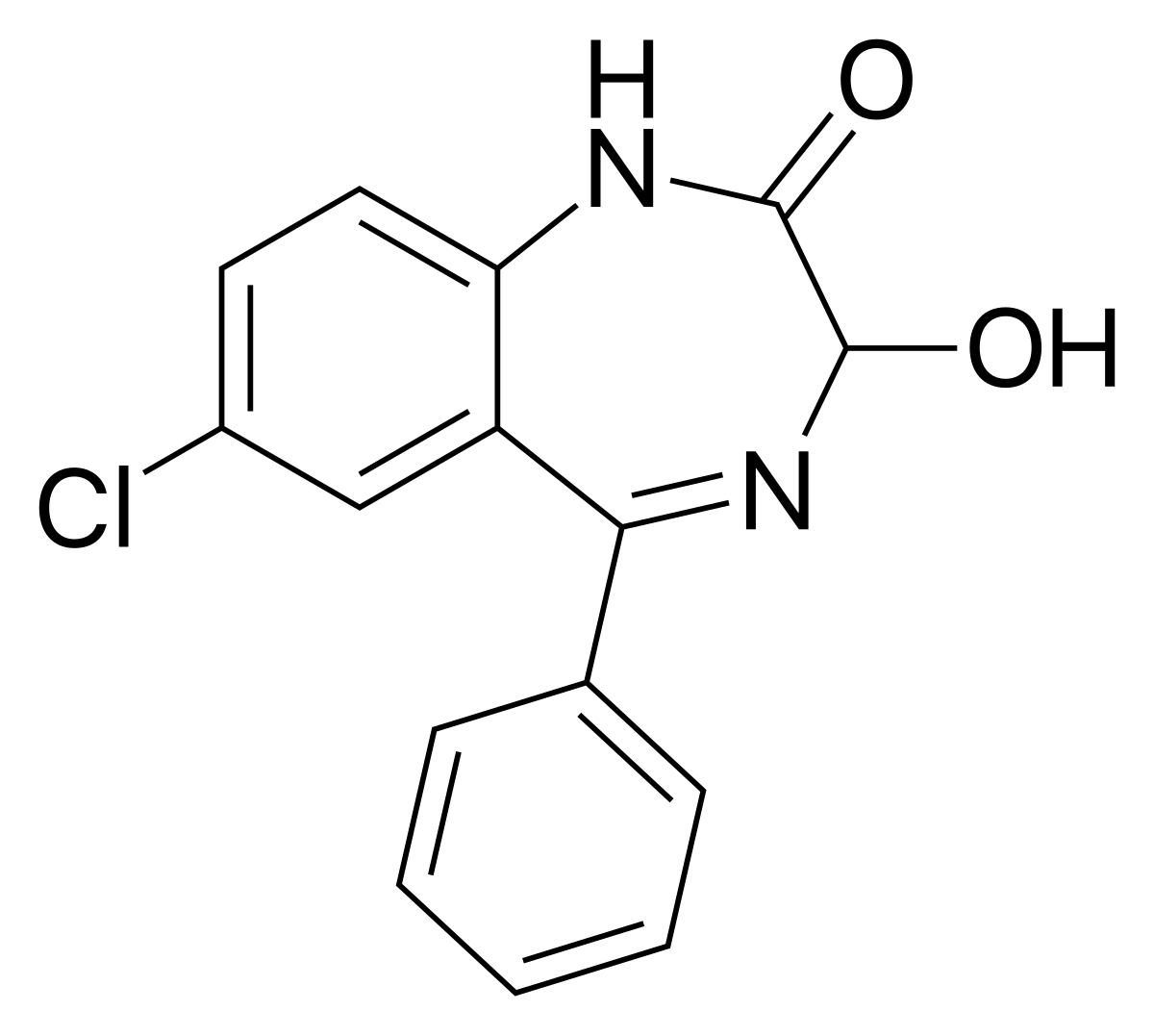 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Specifically Kanamycin binds to four nucleotides of 16S rRNA and a single amino acid of protein S12. Clonazepams primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain by the benzodiazepine receptor located on GABA A receptors which in turn leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing. Oxazepam Temazepam Lorazepam Out the Liver. This inhibition decreases cardiac output by producing negative chronotropic and inotropic effects without presenting activity towards membrane stabilization nor intrinsic sympathomimetics. Mechanism of action.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
7- Muscular disorders. Clonazepams primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain by the benzodiazepine receptor located on GABA A receptors which in turn leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing. Unlike benzodiazepines etifoxine may produce its anxiolytic effects through a dual mechanism by directly binding to GABA A receptors and purportedly exact binding site undetermined to the mitochondrial translocator protein TSPO resulting in increases in endogenous neurosteroids. A Beta-1 adrenergic receptor. The consumption of benzodiazepines causes a high muscular relaxation and.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title oxazepam mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.