Risk assessment project on flourides
Risk Assessment Project On Flourides. F H 2 O. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride.
 Pdf Health Risk Assessment Of Fluoride Exposure In Soil Plants And Water At Isfahan Iran From researchgate.net
Pdf Health Risk Assessment Of Fluoride Exposure In Soil Plants And Water At Isfahan Iran From researchgate.net
It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. F H 2 O.
1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride.
That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. F H 2 O.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. F H 2 O. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. F H 2 O. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. F H 2 O.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
F H 2 O. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. F H 2 O.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. F H 2 O. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. F H 2 O. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. F H 2 O. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride.
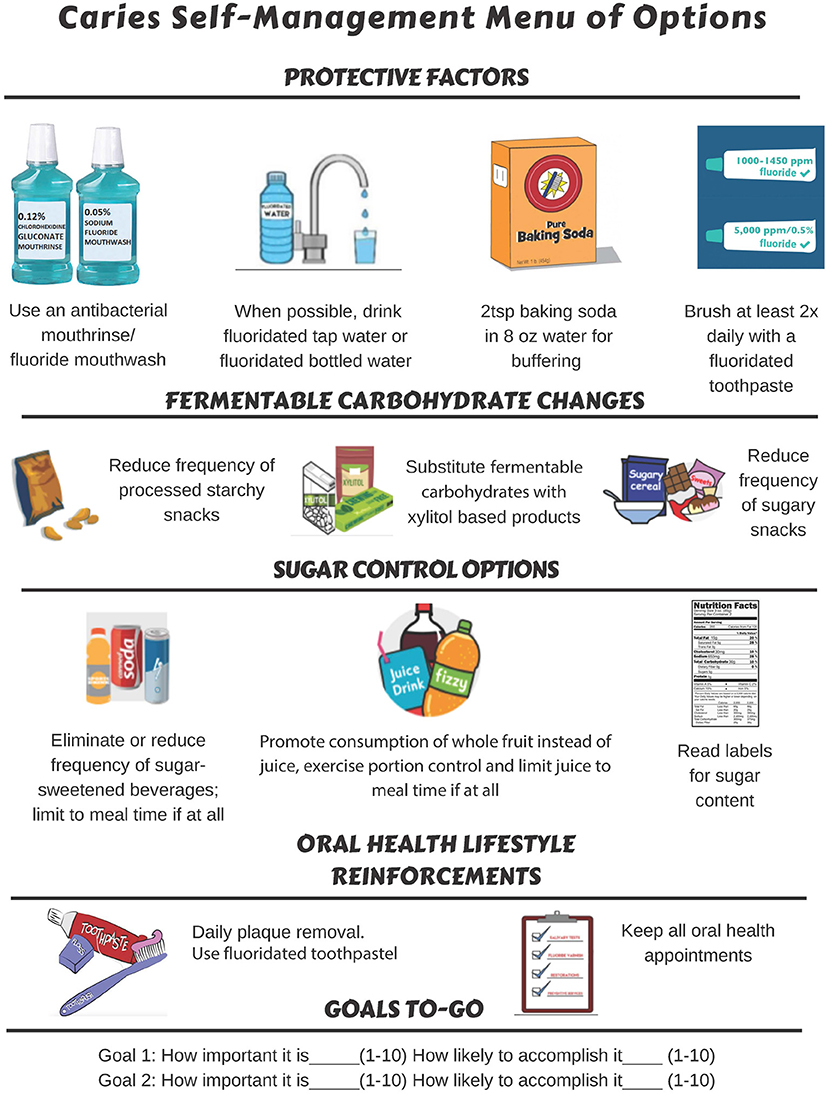 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. F H 2 O. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. F H 2 O. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. It is therefore a weak base and tends to remain as the fluoride ion rather than generating a substantial amount of hydrogen fluoride. In aqueous solution fluoride has a p K b value of 108. That is the following equilibrium favours the left-hand side in water. 1 This neutralization reaction forms hydrogen fluoride HF the conjugate acid of fluoride.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title risk assessment project on flourides by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





