What is dangerous about potassium chlorate
What Is Dangerous About Potassium Chlorate. However when gummy bears are dropped into potassium chlorate and a drop of sulfuric acid added as a catalyst the two chemicals react violently with each other releasing large quantities of. It is appreciably soluble in water and heavier so may be expected to sink and dissolve at a rapid rate. NFPA Class 4 Oxidizers. B Packing Group II if the criteria for Packing Group I are not met and the test sample exhibits an average.
 Potassium Chlorate A Chemical Compound Assignment Point From assignmentpoint.com
Potassium Chlorate A Chemical Compound Assignment Point From assignmentpoint.com
Less than the mean burning time of a 32 potassium bromatecellulose mixture by mass when test O1 is used or ii greater than the mean burning rate of a 31 calcium peroxidecellulose mixture by mass when test O3 is used. Potassium iodide KI is the only pharmaceutical intervention that is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating 131I- exposure a common radioactive fission product. Polymerization of acetaldehyde. Although it is not itself flammable the solid product and even 30 solutions in water are powerful oxidizing agents. B Packing Group II if the criteria for Packing Group I are not met and the test sample exhibits an average. A few examples of this potentially dangerous storage method are demonstrated by the following pairs of incompatible materials.
Sulphuric acid H2SO4 will burn any organic material.
Some chemicals gases liquid. Sodium chlorite greater than 40 by weight sodium dichloroisocyanurate. NFPA Class 4 Oxidizers. Examples of NFPA Class 4 oxidizers include. Most of the explosives are dangerous and poisonous ie. Though effective KI administration needs to occur prior to or as soon as possible within a few hours after radioactive exposure to maximize the radioprotective benefits of KI.
 Source: milled.com
Source: milled.com
Phosphors burn at 25oC and catch fire upon touching. Sodium chlorite greater than 40 by weight sodium dichloroisocyanurate. It is appreciably soluble in water and heavier so may be expected to sink and dissolve at a rapid rate. Less than the mean burning time of a 32 potassium bromatecellulose mixture by mass when test O1 is used or ii greater than the mean burning rate of a 31 calcium peroxidecellulose mixture by mass when test O3 is used. Some chemicals gases liquid.
 Source: acs.org
Source: acs.org
Phosphors burn at 25oC and catch fire upon touching. A few examples of this potentially dangerous storage method are demonstrated by the following pairs of incompatible materials. Potassium chlorate. Some chemicals gases liquid. Less than the mean burning time of a 32 potassium bromatecellulose mixture by mass when test O1 is used or ii greater than the mean burning rate of a 31 calcium peroxidecellulose mixture by mass when test O3 is used.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Some chemicals gases liquid. Though effective KI administration needs to occur prior to or as soon as possible within a few hours after radioactive exposure to maximize the radioprotective benefits of KI. Potassium cyanide if injected into the bloodstream. Copper II sulfide and cadmium chlorate. Sodium exposed to moist air will explode.
 Source: simple.wikipedia.org
Source: simple.wikipedia.org
Examples of NFPA Class 4 oxidizers include. Acetic acid and acetaldehyde. Ammonium perchlorate particle size greater than 15 microns ammonium permanganate. Some chemicals gases liquid. Contact with wood organic matter ammonium salts sulfur sulfuric acid various metals and.
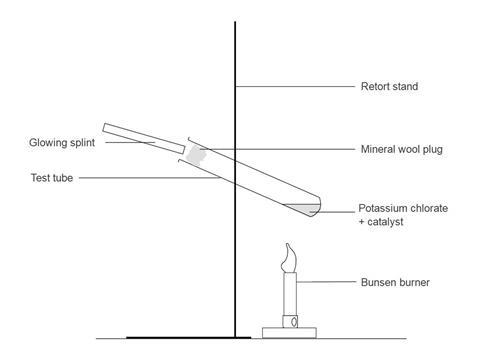 Source: edu.rsc.org
Source: edu.rsc.org
Less than the mean burning time of a 32 potassium bromatecellulose mixture by mass when test O1 is used or ii greater than the mean burning rate of a 31 calcium peroxidecellulose mixture by mass when test O3 is used. Copper II sulfide and cadmium chlorate. Sodium nitrite and sodium thiosulfate. A few examples of this potentially dangerous storage method are demonstrated by the following pairs of incompatible materials. Potassium chlorate KClO3 explodes by rubbing it.
 Source: hackaday.com
Source: hackaday.com
Phosphors burn at 25oC and catch fire upon touching. Copper II sulfide and cadmium chlorate. Ammonium perchlorate particle size greater than 15 microns ammonium permanganate. A few examples of this potentially dangerous storage method are demonstrated by the following pairs of incompatible materials. Potassium cyanide if injected into the bloodstream.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Some chemicals gases liquid. It is appreciably soluble in water and heavier so may be expected to sink and dissolve at a rapid rate. Potassium chlorate. Sodium exposed to moist air will explode. NFPA Class 4 Oxidizers.
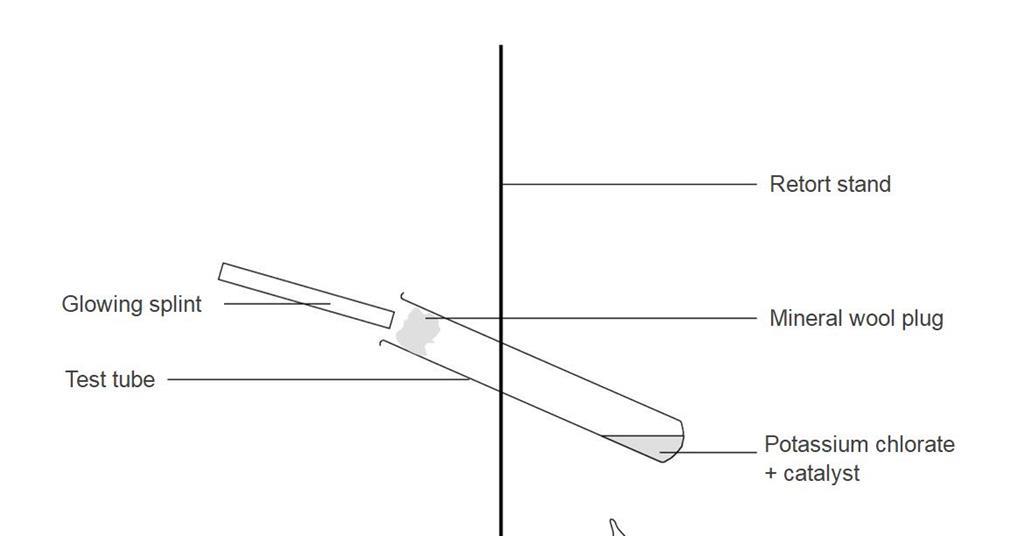 Source: edu.rsc.org
Source: edu.rsc.org
Sulphuric acid H2SO4 will burn any organic material. Most of the explosives are dangerous and poisonous ie. Acetic acid and acetaldehyde. Sulphuric acid H2SO4 will burn any organic material. Contact with wood organic matter ammonium salts sulfur sulfuric acid various metals and.
 Source: assignmentpoint.com
Source: assignmentpoint.com
NFPA Class 4 Oxidizers. Sulphuric acid H2SO4 will burn any organic material. Explosive when heated. Sodium nitrite and sodium thiosulfate. Hydrogen peroxide and iron II sulfide.
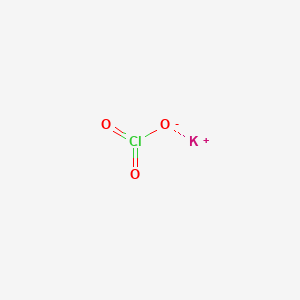
Although it is not itself flammable the solid product and even 30 solutions in water are powerful oxidizing agents. Copper II sulfide and cadmium chlorate. Sulphuric acid H2SO4 will burn any organic material. Acetic acid and acetaldehyde. Explosive when heated.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is dangerous about potassium chlorate by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.